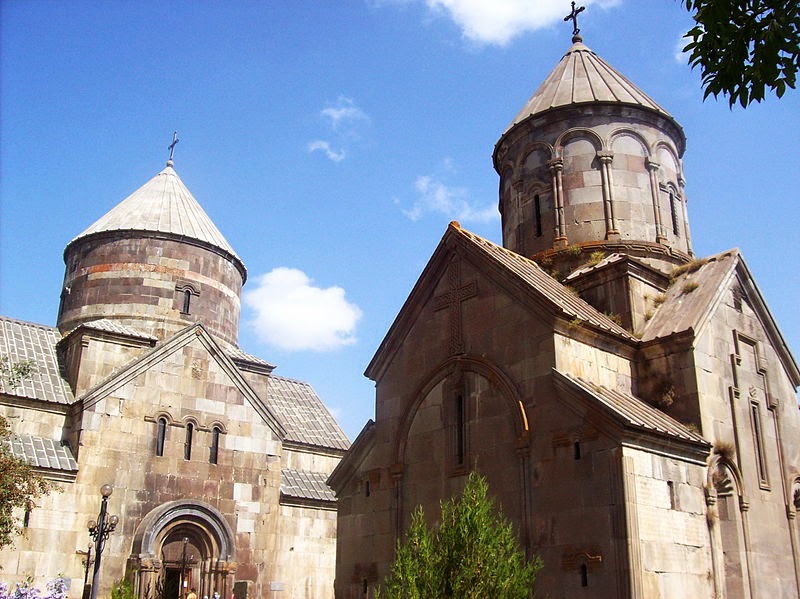
Kecharis (Armenian: Կեչառիս) is an 11-13th-century monastery, located 60 km from Yerevan, in the ski resort town of Tsakhkadzor in Armenia. Nestled in the Bambak mountains, Kecharis was founded by a Pahlavuni prince in the 11th century, and construction continued until the middle of the 13th century. In the 12th and 13th centuries, Kecharis was a major religious center of Armenia and a place of higher education. Today, the monastery has been fully restored and is clearly visible from the ski slopes.
Badly damaged in an earthquake of 1927, reconstruction was not begun by the Armenian SSR until the 1980s. A series of nationwide problems led to a halt in reconstruction for about a decade as the 1988 Armenian earthquake hit, the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, the Nagorno-Karabakh War broke out, and Armenia was blockaded by its two Turkic neighbors. As Armenia recovered slowly from these catastrophes, the reconstruction of Kecharis finally resumed in 1998 and finished in 2000 thanks to a donation by an Armenian benefactor from Vienna named Vladimir Harutyunian, in memory of his parents Harutyun and Arsenik.
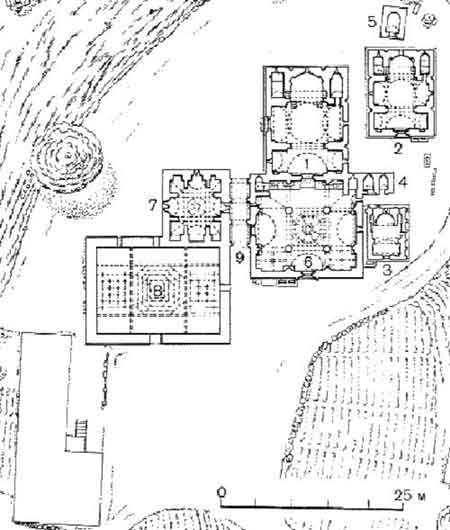
Complex
The main group of the complex consists of three churches, two chapels and a gavit, to the west of which, a few dozen meters away, there is another church with its own vestry at the side of a road leading to the forest. There still are many tombstones around these monuments.
Saint Grigor Church
The main temple, the church of Saint Grigor, is the monastery's first structure erected by Grigor Magistros Pahlavuni in 1003. Being of a domed hall type, it is one of the typical church structures of the period of developed feudalism in Armenia. The interior of the temple is divided into three spaces by two pairs of wall-attached abutments. The central (and largest) space of the church is crowned by a broad cupola resting on spherical pendentives. The cupola and pendentives were destroyed by an earthquake in 1927, and reconstructed in 2000.
The semicircular altar apse has two-storey vestries on either side. Three triangular niches behind the altar provide openings for light. The sole of the altar has carved geometrical ornament, alternating with rosettes in places.
Surp Nshan Church
The church of Surp Nshan (Armenian: Սուրբ Նշան, "Holy Sign of Cross" in Armenian), situated south of the church of Grigor, is a small cross-winged domed structure built, judging by the type of the building and by architectural details, in the 11th century, probably soon after the church of S. Grigor.
Katoghike Church
The Katoghike (Cathedral) church stands south of S. Nshan, with a narrow passage dividing them. Judging by an inscription, it was built under Prince Vasak Khakhpakyan of the Proshyan clan (in the first quarter of the 13th century) by the architect Vetsik, in whose memory a khachkar, ornamented with highly artistic carving, was put up a little south of the church.
The Katoghike church belongs to the cross-winged domed type and has two-story annexes in all the four corners of the prayer hall. The entrances to the upper eastern annexes are from the side of the altar apse. Stone cantilever stairs lead to the western annexes of the first floor.
The character of Katoghike church's decoration is connected with the artistic traditions of the time when it was built. The round cupola drum was destroyed by earthquake in 1927 (also rebuilt in by 2000), and is decorated with a 12-arch arcature. The front wall of the altar has carved khachkar-type crosses, and there are rosettes on the walls and on the spherical pendentives of the cupola where they alternate with flat arch motives.
Gavit
The gavit, built in the second half of the 12th century and attached to the western facade of S. Grigor church, is an early structure of this type. The rectangular hall is divided into nine sections by four heavy free-standing columns.
The eastern corners of the interior are taken up by small two-storey annexes which first appeared in this form in this gavit.
The architectural details of the building are rather modest. The small windows are topped by profiled edges above which there are, in the middle window of the southern facade, octafoil rosettes and sun dials, widespread in Armenia and, on the western facade, jugs. As distinct from the portals of the churches, the only western entrance is built as a rectangular opening with a niche framed with bunches of small columns and an arch. In the interior, the fine geometrical ornaments on the capitals of the columns and on the cornice of the tent base immediately catch the eye.
Chapels
The chapels situated between the churches of Grigor and Surp Nshan were small rectangular ones, with an altar apse and vaulted ceilings. The chapel adjacent to the church of Gregory served as the burial vault of Grigor Magistros Pahlavuni, which means that it was built in the early 11th century. The chapels were united by a small vaulted premise in which classes were probably conducted for the school's students.
Surp Harutyun
The church of Surp Harutyun (Holy Resurrection), standing on a forest glade, away from the main group, was built by a son of Hasan in 1220. This is a small, outwardly rectangular. domed-hall church with a lofty cupola. The only entrance, with a small vestry in front of it, is from the west. As distinct from the ordinary vestries, it has a vaulted ceiling, and is narrower than the church. A distinctive feature of the structure is that it has, on its western facade, twin openings topped with arches which rest on the wall-attached and intermediate columns. This gives the structure the appearance of an open passage. There are many graves in the church which was probably a family burial vault.





























.jpg)